บทความ
ทำความรู้จัก POL (Polygon) ที่เน้นเรื่องปรับขนาด ช่วยให้ Ethereum เร็วขึ้น ลดต้นทุนค่าธรรมเนียม

หากคุณกำลังสงสัยว่าเหรียญบน Bitkub Exchange อย่าง POL (Polygon) คืออะไร ใครเป็นผู้สร้าง และมีโครงสร้างอะไรที่น่าสนใจบ้าง บทความนี้จะพาคุณไปรู้จักกับ POL ให้มากขึ้น!
เหรียญ POL (Polygon) คืออะไร
เหรียญ POL เดิมมีชื่อเรียกว่า MATIC โทเคนมาตรฐาน ERC-20 หมายความว่ามันเข้ากันได้กับสกุลเงินดิจิทัลอื่นๆ ที่ใช้ Ethereum ก่อนจะเกิดกระบวนการย้ายโทเคนจาก MATIC มาเป็น POL เมื่อวันที่ 4 กันยายน 2024 จากความเห็นพ้องกันของชุมชน ที่อัปเกรดโทเคนให้เป็น Utility Token ที่มีแนวทางการทำงานที่เรียกว่า “Hyperproductive Token” ที่สามารถดำเนินการได้มากกว่าการรักษาความปลอดภัยของเครือข่าย ในระยะแรกของการพัฒนาทำให้ POL เข้ามาแทนที่ในฐานะแก๊สโทเคนสำหรับการทำธุรกรรม และใช้สำหรับการทำ Staking บน Polygon PoS
การทำงานของ Polygon
ระบบ Proof-of-Stake ของ Polygon มีกลไกพิเศษที่สามารถถอนสินทรัพย์ที่วางค้ำประกันไว้ เรียกว่า Heimdall ที่จะคอยสอดส่องรักษาความมั่นคงของระบบ และป้องกันการโกงที่อาจมาในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ อาทิ การตั้งใจตรวจสอบข้อมูลผิด ๆ เพื่อบิดเบือนข้อมูลของบล็อกเชน เป็นต้น
อีกสองกลไกสำคัญคือ Plasma และ Polygon SDK ที่ทำงานร่วมกันเหมือนโครงสร้างรับรองการขยายตัวของบล็อกเชน Polygon จึงเป็นที่สนใจของหลาย ๆ โปรเจกต์บล็อกเชนที่ต้องการขยายเครือข่าย โดย Plasma ช่วยให้บล็อกเชนสามารถรับรอง Decentralized Applications (DApps) หรือ Decentralized Finance (DeFi) ได้อย่างไม่จำกัด พร้อมปลดล็อกข้อจำกัดต่าง ๆ ในระบบดั้งเดิมอย่าง Proof of Work
Polygon 2.0
ข้อมูลจาก White paper ระบุถึงกระบวนการเปลี่ยนแปลง MATIC สู่ POL เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของการยกระดับประสิทธิภาพของระบบนิเวศ Polygon ครั้งใหญ่ ที่เรียกว่า “Polygon 2.0” ที่เปิดตัวเมื่อวันที่ 12 มิถุนายน 2024 ยกระดับเป็นบล็อกเชน Layer-2 ที่ขับเคลื่อนด้วย zero-knowledge (ZK) rollup ที่มีความสามารถในการทำงานแบบข้ามเครือข่าย (cross-chain) ซึ่งช่วยด้านความปลอดภัย ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และช่วยแก้ไขในการสภาพคล่อง
โดย Polygon 2.0 เป็นความร่วมมือกันระหว่าง Polygon Labs นักพัฒนา นักวิจัย แอปพลิเคชัน ผู้ควบคุมโหนด (Node) ผู้ตรวจสอบ (Validator) และชุมชน Polygon และ Ethereum ผ่านการอภิปรายใน Forum ของชุมชน
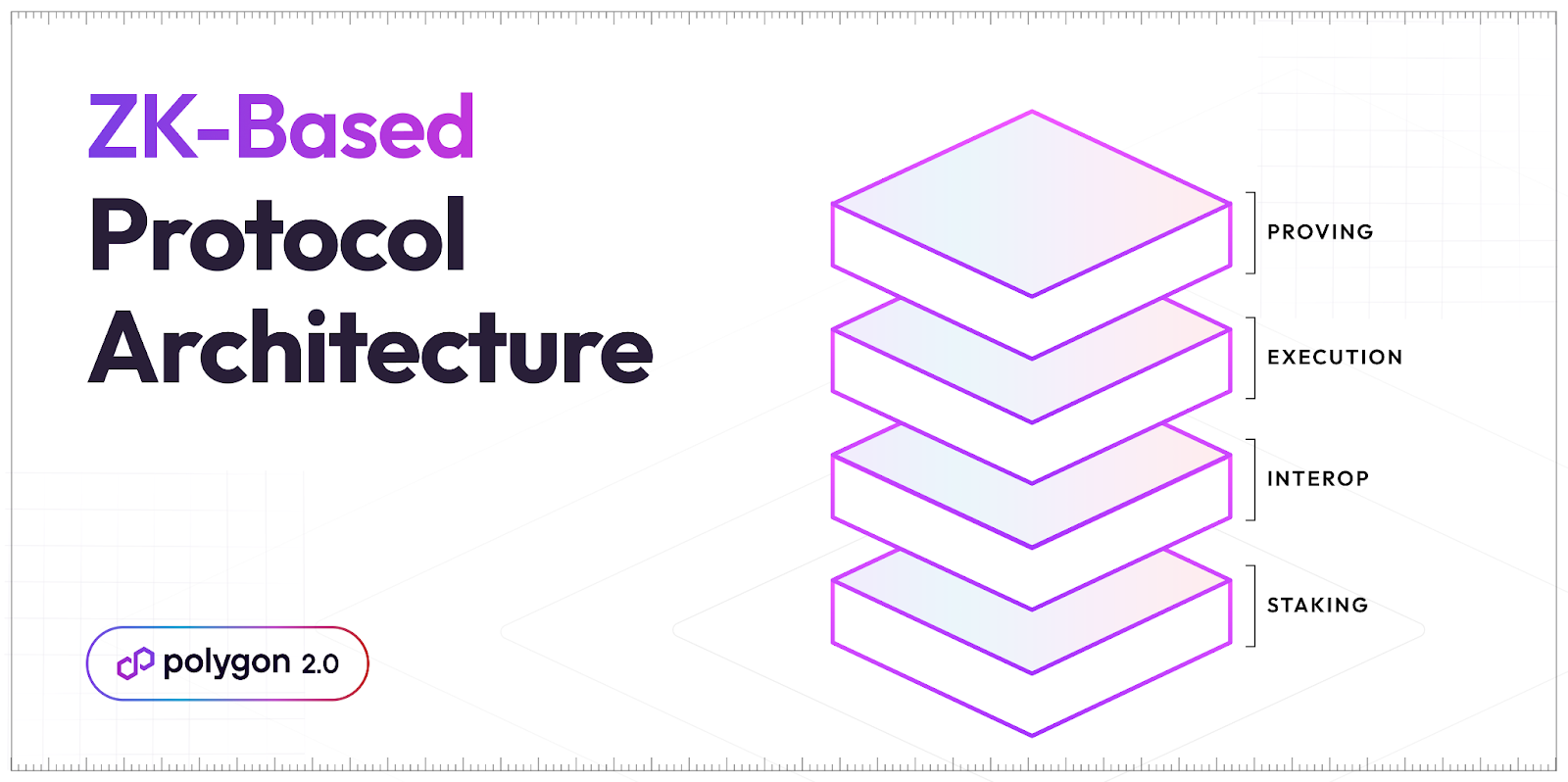
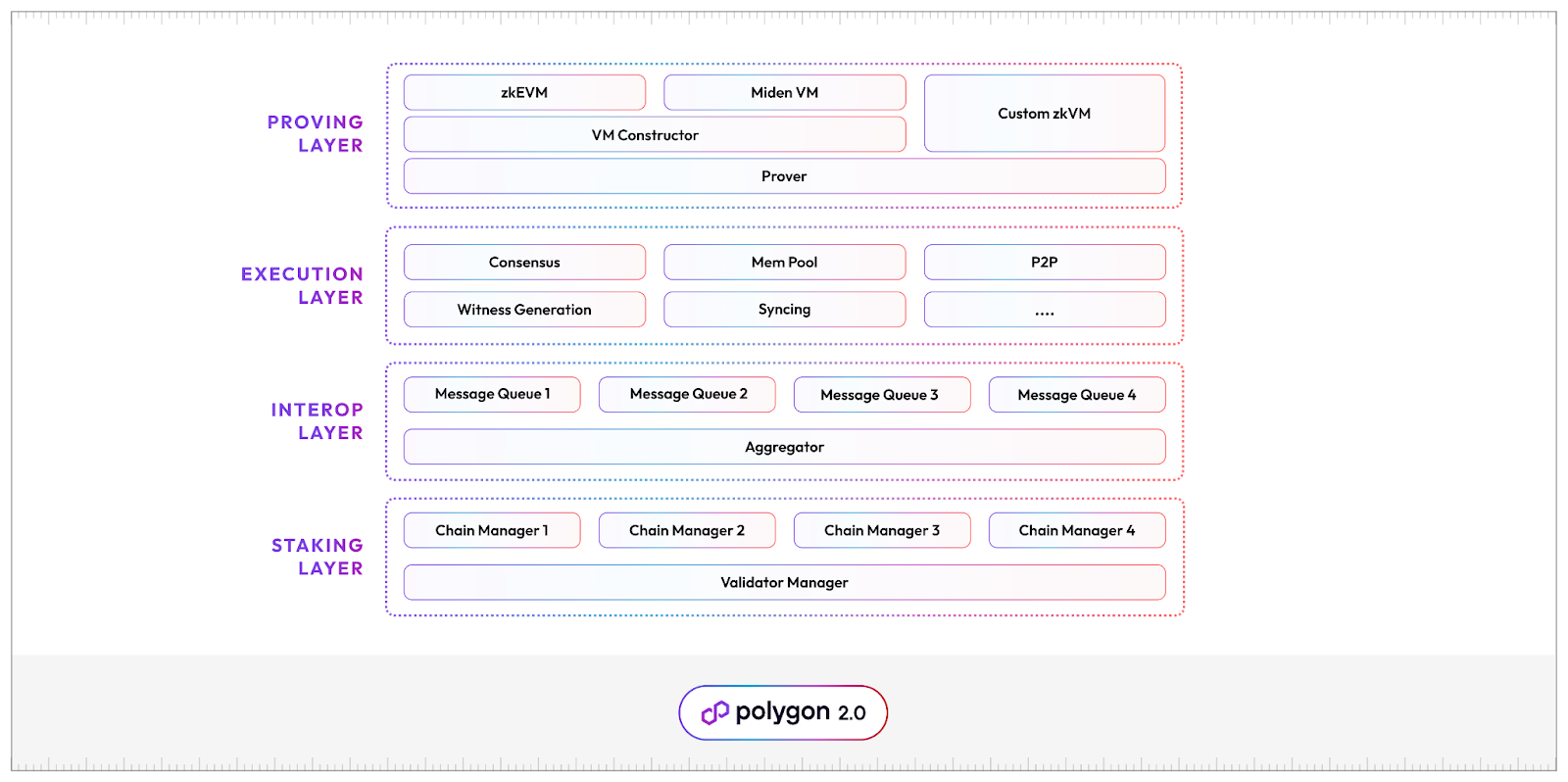
นอกจากนี้ยังเห็นได้ว่ากระบวนการอัปเกรดนี้เป็นกระบวนการที่เกิดขึ้นอย่างค่อยเป็นค่อยไป ที่มีลำดับขั้น ซึ่งการเปลี่ยนจาก MATIC สู่ POL ยังเป็นอีกส่วนหนึ่งของการเตรียมความพร้อม ของ Polygon 2.0 ในด้าน Protocol Architecture เป็นสถาปัตยกรรมที่กำหนดรูปแบบของชั้นโปรโตคอลเพื่อทำงานร่วมกัน ทั้งหมด 4 ชั้นคือ Staking Layer, Agg Layer, Execution Layer, Proving Layer สำหรับรองรับการทำงานของ Agg Layer หรือ Aggregation Layer ที่จะเข้ามามีบทบาทสำคัญในการบริหารการเชื่อมโยงเครือข่ายในอนาคต
กล่าวคือ Aggregation Layer เป็นส่วนของการส่งข้อความข้ามเครือข่ายในระบบนิเวศ Polygon ช่วยให้เกิดความราบรื่นปลอดภัย โดยเลเยอร์นี้จะช่วยลด ลดความซับซ้อนของการสื่อสารข้ามเครือข่าย และทำให้เครือข่าย Polygon ทั้งหมดรู้สึกเหมือนเป็นเครือข่ายเดียว
ทีมผู้สร้าง Polygon

Jaynti Kanani — โดยก่อนที่จะมาร่วมก่อตั้ง Polygon (เดิมชื่อเครือข่าย Matic) Kanani ทำงานเกี่ยวกับ Blockchain Engineer มาก่อน และในช่วงที่เกิดกระแส CryptoKitties เขาก็มองเห็นถึงปัญหาด้านการขยายเครือข่ายของ Ethereum จึงได้แชร์มุมมองของเขาร่วมกับ Sandeep Nailwal และ Anurag Arjun จากนั้นจึงได้ร่วมกันก่อตั้ง Matic ขึ้นในช่วงต้นปี 2018
Sandeep Nailwal — Nailwal ทำงานในสายอาชีพ Software Engineer และในปี 2015 เขาก็ได้เปิดตัวโปรเจกต์ ScopeWeaver ซึ่งเป็นตลาดซื้อขายบริการโดยมืออาชีพที่ใหญ่ที่สุดในอินเดีย และยังเป็นตลาดที่นำบล็อกเชนมาใช้เป็นโครงสร้าง ส่วนก่อนหน้านี้เขาเคยร่วมงานกับบริษัทชื่อดังมากมาย เช่น Welspun บริษัทสิ่งทอที่ใหญ่ที่สุดในเอเชีย และเคยเป็นที่ปรึกษาให้ Deloitte
Anurag Arjun — มีประสบการณ์ด้านการบริหารผลิตภัณฑ์ซอฟท์แวร์มานานตั้งแต่ในปี 2006 และเคยร่วมงานกับบริษัทระดับแนวหน้าของอินเดียมากมาย เช่น เคยเป็น Product Manager ให้กับ Dexter Consultancy ในปี 2008 จากนั้นในปี 2013 เขาได้ร่วมงานกับ IRIS Business Services ในตำแหน่ง Associate Vice President of Product Management โดยเขามีบทบาทสำคัญในการพัฒนาผลิตภัณฑ์ของบริษัทฯ ให้มี UX ที่ลื่นไหลและประสิทธิภาพโดยรวมที่สูงยิ่งขึ้น
Mihailo Bjelic — อีกหนึ่งผู้ร่วมก่อตั้งของ Polygon โดย Mihailo จบการศึกษาในสาขา Information Systems Engineer จาก University of Belgrade ซึ่งเขาเป็นหนึ่งใน Ethereum Researcher ที่มีอิทธิพลและใกล้ชิดกับชุมชนของ Ethereum มากที่สุดคนหนึ่ง
หน้าที่ของโทเคน POL
POL เป็น โทเคนดั้งเดิมของ Polygon ที่ให้ผู้ใช้งานสามารถโต้ตอบกับ DApps กว่าหมื่นรายการบนบล็อกเชนของ Polygon นอกจากนี้ยังใช้เพื่อรักษาความปลอดภัยเครือข่ายผ่าน Staking อีกด้วย
— โทเคนใช้จ่ายค่าธรรมเนียม (Gas Token) การใช้งานหลักของ POL คือใช้จ่ายค่าธรรมเนียมที่เกิดจากการทำธุรกรรมต่าง ๆ หรือใช้แอปพลิเคชันที่สร้างบน Polygon PoS นอกจากนี้ POL ยังทำให้ผู้ตรวจสอบ มีแรงจูงใจในการประมวลผลและตรวจสอบธุรกรรม ซึ่งจะทำให้มั่นใจได้ว่าเครือข่ายยังคงทำงานและปลอดภัย
.
— โทเคนด้านความปลอดภัยของเครือข่าย Polygon ใช้กลไก (Proof-of-Stake) ซึ่งใช้ POL ที่มีการ Staking เอาไว้บนเครือข่าย โดยการถือ POL จะช่วยให้เกิดการรักษาความปลอดภัย ของ Polygon PoS และรับรางวัลตอบแทน ผู้ตรวจสอบจะลดแรงจูงใจหากมีความพฤติกรรมที่เป็นอันตราย ซึ่งจะช่วยรักษาความสมบูรณ์ของเครือข่าย
.
— Governance Token สำหรับ Polygon PoS ผู้ตรวจสอบ หรือ Validator มีบทบาทสำคัญ โดยมีการใช้ Polygon Improvement Proposals (PIPs) และการมีส่วนร่วมตามหลักของการกระจายอำนาจ เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าเครือข่ายนั้นดำเนินการไปตามตามฉันทามติของชุมชน
.
— Community Fuel โทเคน POL ใช้เพื่อขับเคลื่อนการเติบโตอย่างยั่งยืนผ่านรูปแบบ emission model โดยส่วนหนึ่งของการปล่อยโทเคน จะถูกนำไปใช้เป็นเงินทุนสำหรับการโครงการที่มีการขับเคลื่อนโดยชุมชน เพื่อสนับสนุนการพัฒนาอย่างต่อเนื่องบนเครือข่าย Polygon
.
— Hyperproductive Token เป็นโทเคนที่มีประสิทธภาพสูงสุด ช่วยให้ผู้ตรวจสอบสามารถรักษาความปลอดภัยให้กับเชนหลาย ๆ แห่ง และมีบทบาทหลายแบบบนเครือข่าย Polygon แนวทางนี้ข่วยเพิ่มความปลอดภัย และความสามารถในการปรับขนาดและประสิทธิโดยรวม
การกระจายโทเคนของ POL
โทเคน POL หรือ MATIC ดั้งเดิม ถูกสร้างออกมาให้มีอุปทานจำกัดที่ 10,000,000,000 POL โดยจะค่อย ๆ ถูกปล่อยออกมาเป็นรายเดือนจนถึงเดือนธันวาคม ค.ศ. 2022
สำหรับการกระจายโทเคน MATIC (เดิม) มีรายละเอียดดังต่อไปนี้
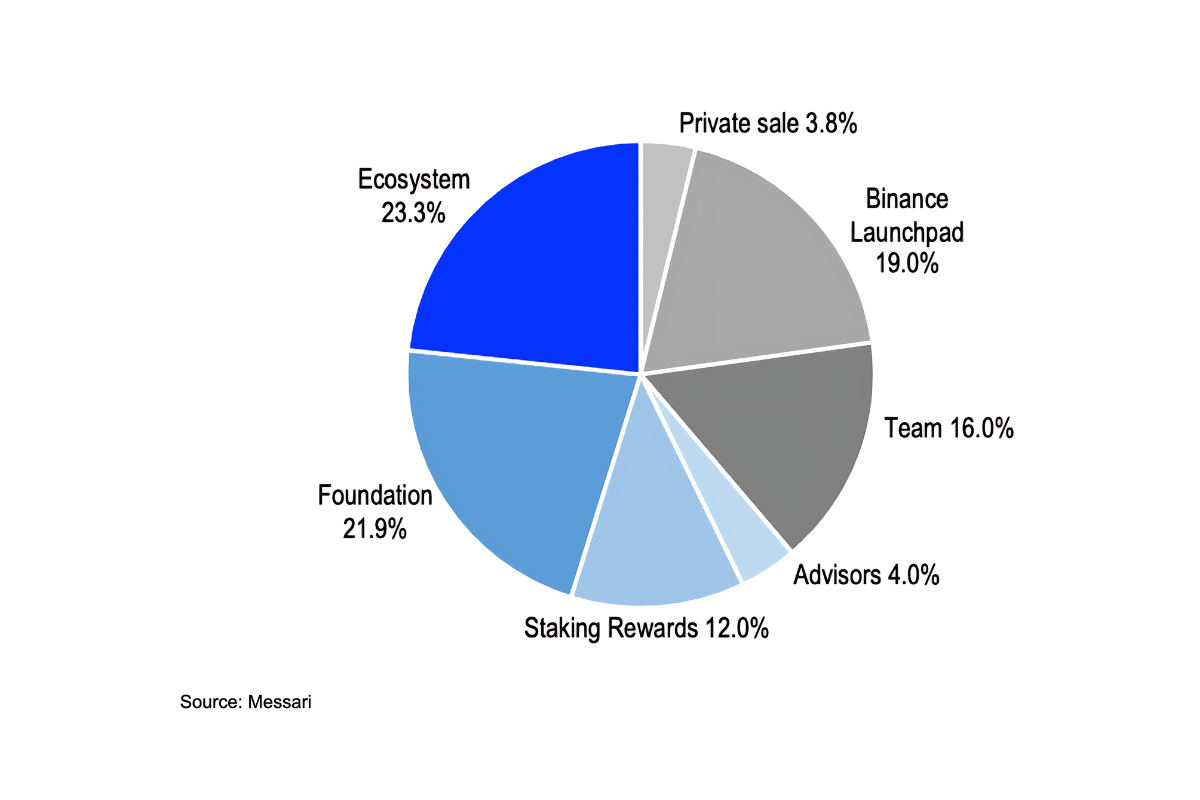
-รอบ Private Sale: 3.80% จากอุปทานทั้งหมด
-เสนอขายแบบ IEO (Initial Exchange Offering): 19%
-ทีมผู้พัฒนา: 16%
-ทีมที่ปรึกษา: 4%
-สำหรับการทำงานของเครือข่าย: 12%
-สำหรับมูลนิธิ:21.86%
-สำหรับระบบนิเวศ: 23.33%
แต่เมื่อมีการอัปเกรด จาก MATIC เป็น POL ด้วยอัตรา 1:1 มีเวลาดำเนินเป็นเวลา 4 ปี และมีเหรียญเพิ่มขึ้น 200 ล้านเหรียญต่อปี หรือประมาณ 2% ต่อปีต่อเนื่องเป็นเวลา 10 ปี เพื่อรองรับการเติบโต โดยแบ่งสัดย่อย หรือ Emission Rate ออกเป็น 2 ส่วน คือ
— Validators Rewards คิดเป็น 1% ต่อปี เพื่อสร้างแรงจูงใจในการรับและรักษาผู้ตรวจสอบไว้บนเครือข่าย
.
— Ecosystem Support คิดเป็น 1% ต่อปี เพื่อให้การสนับสนุนอย่างต่อเนื่องสำหรับการพัฒนาและการเติบโตต่อไปของระบบนิเวศ Polygon
ข้อมูลด้านราคาของ POL
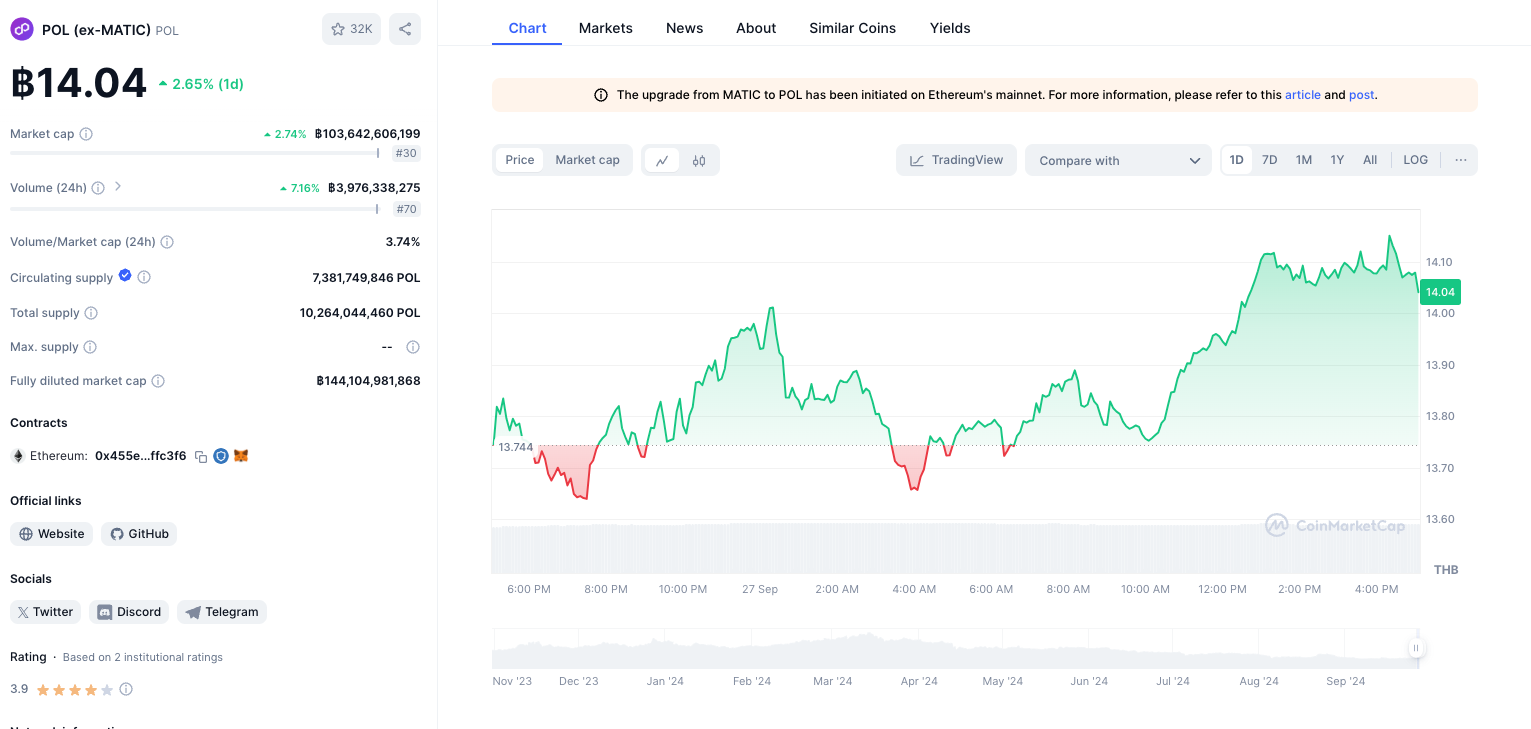
ข้อมูลจากเว็บไซต์ Coinmarketcap เมื่อวันที่ 4 พฤศจิกายน 2024 โทเคน POL มีมูลค่าตามราคาตลาด (Market cap) ที่ 2,279,315,202 ดอลลาร์สหรัฐฯ หรือประมาณ 76,916,049,715 บาท
ณ เวลาที่เขียนบทความนี้ โทเคน POL ซื้อขายกันอยู่ที่ราคาประมาณ 0.2979 ดอลลาร์สหรัฐฯ หรือประมาณ 10.05 บาท ต่อ 1 POL โดย โทเคน POL เคยทำราคาสูงสุด (All-time high) ที่ 1.29 ดอลลาร์สหรัฐฯ หรือประมาณ 43.38 บาท เมื่อวันที่ 14 มีนาคม 2024
อ้างอิง Polygon, Polygon MATIC to POL, The Block, YBB Capital Medium, Coinmarketcap, Coinbase
**บทความนี้แก้ไขเปลี่ยนแปลงล่าสุดเมื่อวันที่ 4 พฤศจิกายน 2024
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
คำเตือน:
-สินทรัพย์ดิจิทัลมีความเสี่ยง โปรดศึกษาและลงทุนให้เหมาะสมกับระดับความเสี่ยงที่ยอมรับได้
-ผลตอบแทนของสินทรัพย์ดิจิทัลในอดีตหรือผลการดําเนินงานในอดีต มิได้เป็นสิ่งยืนยันถึงผลตอบแทน ของสินทรัพย์ดิจิทัลหรือผลการดําเนินงานในอนาคต
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
What is the POL (Polygon)?

The POL token, formerly known as MATIC, is a utility token built on the Ethereum blockchain. It was originally introduced as an ERC-20 standard token but underwent a significant upgrade in September 2024. This upgrade transformed POL into a “Hyperproductive Token,” enabling it to perform a broader range of functions beyond its initial role as a gas token for transactions on the Polygon network.
As a utility token, POL is now used for various purposes within the Polygon ecosystem, including staking to secure the network and facilitating other decentralized applications. This evolution reflects the growing capabilities and versatility of the Polygon platform.
How Polygon Works
Polygon’s Proof-of-Stake system incorporates Heimdall, a unique mechanism enabling the withdrawal of collateral assets. Heimdall safeguards the system’s integrity by detecting and preventing fraudulent activities, such as the deliberate dissemination of false information to manipulate the blockchain.
To enhance scalability, Polygon leverages Plasma and the Polygon SDK as a collaborative framework. This approach has attracted significant interest from blockchain projects seeking to expand their networks. Plasma empowers the blockchain to accommodate an unlimited number of Decentralized Applications (DApps) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) protocols, overcoming the limitations inherent in traditional Proof-of-Work systems.
Polygon 2.0
According to the white paper, the transition from MATIC to POL is a key element of the broader Polygon ecosystem upgrade, known as “Polygon 2.0,” which launched on June 12, 2024. This upgrade leverages a Layer-2 blockchain powered by zero-knowledge (ZK) rollups and cross-chain capabilities, aimed at enhancing security, scalability, and liquidity.
Polygon 2.0 is the result of a collaborative effort involving Polygon Labs, developers, researchers, application creators, node operators, validators, and both the Polygon and Ethereum communities, facilitated through discussions on community forums.
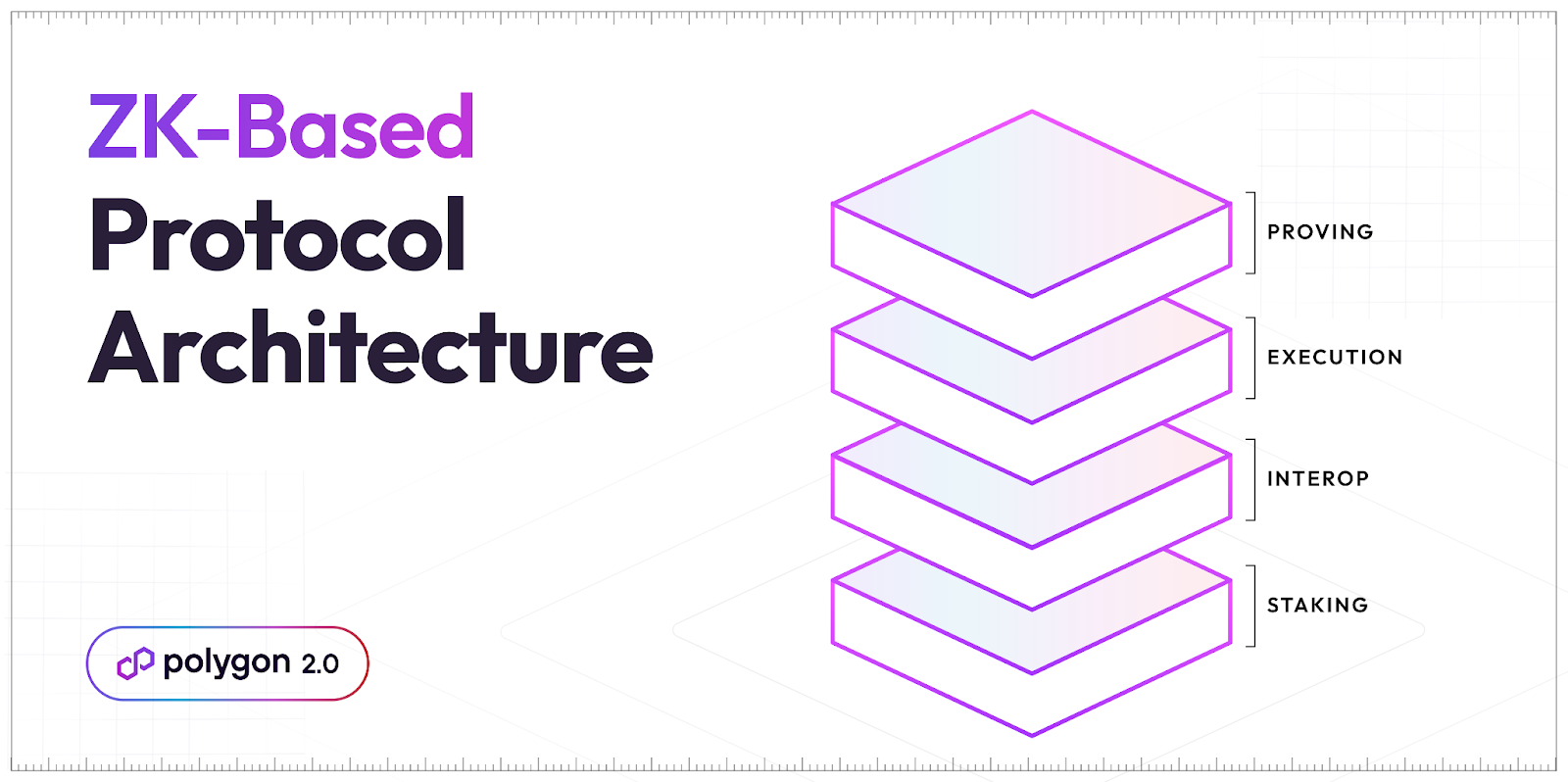
The upgrade process is designed to be gradual and sequential. A key component of Polygon 2.0’s evolution is the transition from MATIC to POL, which plays a pivotal role in the Protocol Architecture. This architecture defines how different protocol layers interact, comprising four key layers: the Staking Layer, Aggregation Layer, Execution Layer, and Proving Layer. The Proving Layer supports the Aggregation Layer, which is set to become crucial for managing network connections in the future.
The Aggregation Layer enables efficient communication across different networks within the Polygon ecosystem, ensuring smoother and more secure interactions. By simplifying cross-network communication, it helps unify the Polygon network, making it operate as a seamless, single entity.
Polygon Team

Jaynti Kanani — Prior to co-founding Polygon (formerly Matic Network), Jaynti Kanani worked as a blockchain engineer. During the CryptoKitties boom, he recognized Ethereum’s scalability challenges and shared these insights with Sandeep Nailwal and Anurag Arjun. Together, they co-founded Matic in early 2018.
Sandeep Nailwal — A software engineer, Sandeep Nailwal launched ScopeWeaver in 2015, India’s largest professional services marketplace built on blockchain infrastructure. He has worked with industry giants like Welspun, Asia’s largest textile company, and served as a consultant for Deloitte.
Anurag Arjun — With extensive experience in software product management since 2006, Anurag Arjun has held key roles in leading Indian companies. In 2008, he worked as a Product Manager at Dexter Consultancy, and in 2013, he joined IRIS Business Services as Associate Vice President of Product Management, where he improved product UX and performance.
Mihailo Bjelic — Another co-founder of Polygon, Mihailo Bjelic holds a degree in Information Systems Engineering from the University of Belgrade. He is a prominent figure within the Ethereum community and a close collaborator with Ethereum researchers.
The Function of the POL
POL is Polygon’s native token used to interact with tens of thousands of dApps on the Polygon blockchain and to secure the network through staking.
— Gas Token: POL is primarily used to pay for fees generated by transactions or applications built on Polygon PoS. It also incentivizes validators to process and verify transactions, ensuring the network’s functionality and security.
— Security Token: Polygon PoS uses a Proof-of-Stake mechanism secured by staked POL. Holding POL helps secure Polygon PoS and earns rewards. Validators are disincentivized for malicious behavior, maintaining network integrity.
— Governance Token: Validators play a key role in Polygon PoS, using Polygon Improvement Proposals (PIPs) and participating in a decentralized manner to ensure the network operates according to community consensus.
— Community Fuel: POL tokens drive sustainable growth through an emission model, where a portion of token emissions funds community-driven projects to support ongoing Polygon development.
— Hyperproductive Tokens: POL tokens are highly efficient, allowing validators to secure multiple chains and play multiple roles on the Polygon network, enhancing security, scalability, and overall efficiency.
Token Supply and Token Distribution
The original POL token, formerly known as MATIC, was designed with a maximum supply of 10 billion POL, which was gradually released monthly until December 2022.
The initial distribution of MATIC tokens was as follows:
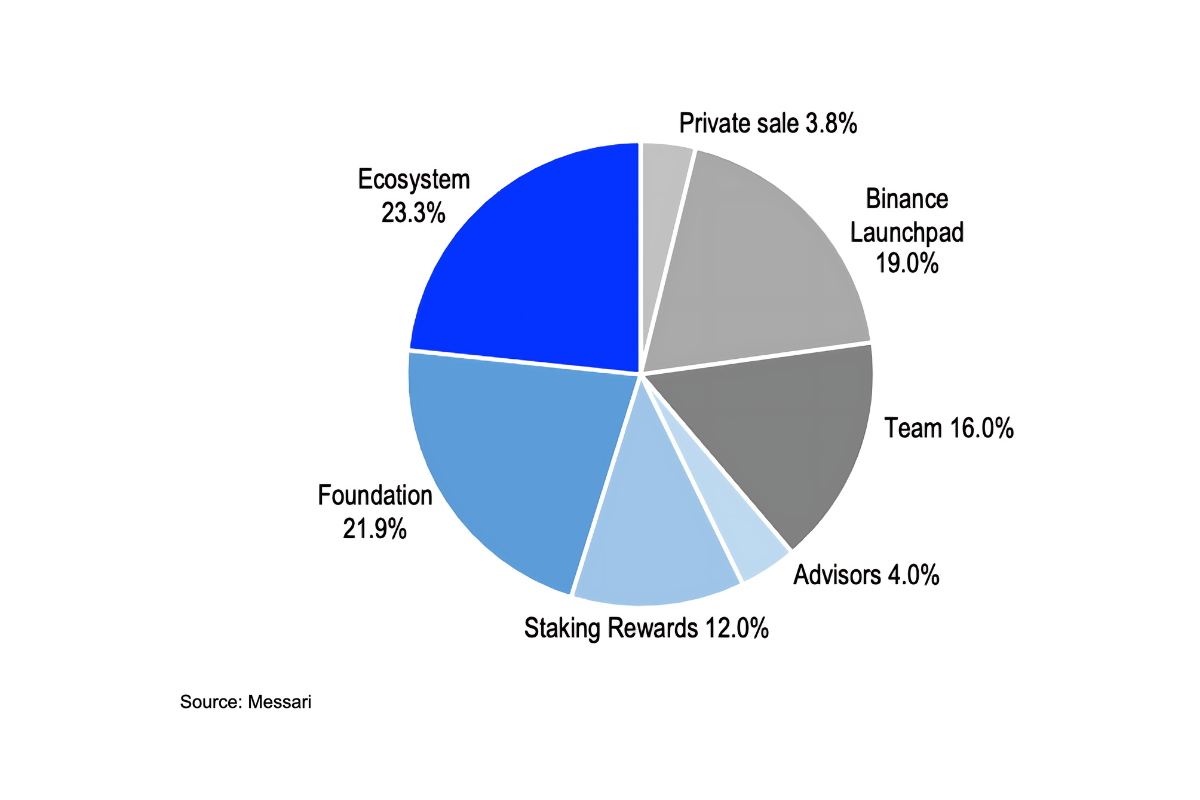
-Private Sale: 3.80% of the total supply
-Initial Exchange Offering (IEO): 19%
-Development Team: 16%
-Advisory Team: 4%
-Network Operations: 12%
-Foundation: 21.86%
-Ecosystem: 23.33%
However, with the 1:1 upgrade from MATIC to POL over four years, an additional 200 million tokens were added annually, representing a 2% annual increase for 10 years to accommodate growth. This additional supply is divided into two categories:
— Validators Rewards: 1% annually to incentivize and retain validators on the network.
— Ecosystem Support: 1% annually to provide ongoing support for the development and growth of the Polygon ecosystem.
Interesting information about POL
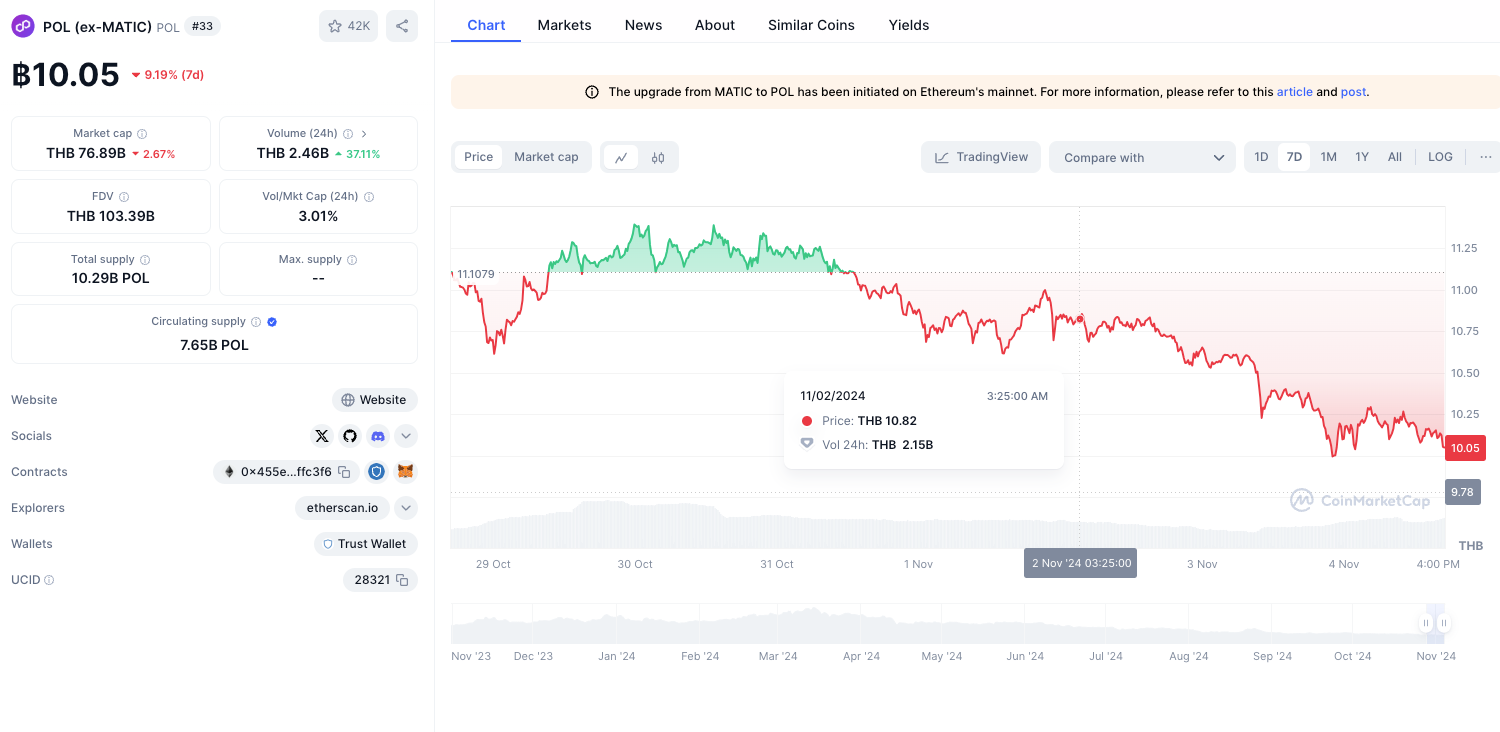
According to Coinmarketcap data on November 4, 2024, the POL token had a market capitalization of US$2,279,315,202, approximately 76,916,049,715 Thai Baht.
At the time of writing, the POL token was trading at around US$0.2979, or approximately 10.05 Thai Baht per POL. The POL token has reached an all-time high of US$1.29, or approximately 43.38 Thai Baht, on March 14, 2024.
Reference: Polygon, Polygon MATIC to POL, The Block, YBB Capital Medium, Coinmarketcap, Coinbase
**This article was updated for latest information on 4 November 2024
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
Disclaimer:
-Digital assets involve risks; investors should study information carefully and make investments according to their own risk profile.
-Past Returns do not guarantee future returns/performance.
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
ที่มา:
Medium